Does a router or modem affect internet speed?

Routers and modems are essential components of home networks. Modems connect your home network to the internet, while routers create a local area network (LAN) and distribute the internet connection to multiple devices wirelessly or via Ethernet cables. Routers allow devices like computers, smartphones and smart TVs to connect to the internet and communicate with each other.
This article explores how routers and modems influence your internet speed, addresses common interference issues and offers practical tips to optimize connectivity.
WiFi that just works!
WiFi plans for any home
Tiny, large or somewhere in between; find WiFi coverage to fit any space. Blanket your entire home with a fast and ultra‑reliable connection.

Understanding routers and modems
Understanding the roles of routers and modems is crucial for maximizing internet speed and reliability. Let’s examine each device’s significance for your home network.
What is a modem?
A modem, also known as a modulator-demodulator, acts as the gateway between the local network and the internet, allowing various forms of online communication and data transfer.
It converts digital data from devices into signals suitable for transmission over various communication channels, such as telephone lines, cable lines or fiber-powered infrastructure used by internet service providers. Simultaneously, it demodulates incoming signals from ISPs into digital data that the devices understand.
What is a router?
A router is a device that connects to the modem and distributes the internet connection to various devices within your home network. It creates a LAN (local area network) and routes the internet traffic between devices on the network, ensuring that data packets transmit to the correct destinations.
The router distributes internet traffic wirelessly via WiFi or through wired Ethernet connections.
How do routers and modems work together?
The modem acts as a gateway to the internet, while the router directs the internet traffic to and from the modem. When you access a website from your device, the router sends the request to the modem, which sends it to the internet through your ISP.
The modem then receives the incoming data and sends it to the router, which routes it to your device, allowing you to access the website’s content.
Many modern devices combine the functions of modems and routers into a single device called a modem-router combo. These devices simplify the setup process and reduce the number of devices needed to set up a home network.
Find your speed
What speed do you need?
Maybe you just need the essentials—or maybe you need to unleash the ultimate internet speed. Explore your options to get the best experience for every device in your home.

How routers affect internet speed
Your router’s capabilities and settings significantly impact your internet connection’s WiFi speeds. Knowing all the factors influencing how well your router handles internet speeds will help you optimize your WiFi speed and reliability. Some of these factors include:
WiFi standards
Different routers support different WiFi standards, with each standard improving speed, WiFi range, device capacity and general performance. Let’s look at the common WiFi standards and their impact on internet speed.
| WiFi Standard | Frequency | Maximum Theoretical Speeds |
|---|---|---|
| 802.11n (WiFi 4) | 2.4 and 5 GHz | 600 Mbps |
| 802.11ac (WiFi 5) | 5 GHz | 3.5 Gbps |
| 802.11ax (WiFi 6) | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz | 9.6 Gbps |
| 802.11ax (WiFi 6e) | 6 GHz | 9.6 Gbps |
| 802.11be (WiFi 7) | 2.4, 5 and 6 GHz | 46 Gbps |
|
WiFi Standard
802.11n (WiFi 4) |
Frequency
2.4 and 5 GHz |
Maximum Theoretical Speeds
600 Mbps |
|
WiFi Standard
802.11ac (WiFi 5) |
Frequency
5 GHz |
Maximum Theoretical Speeds
3.5 Gbps |
|
WiFi Standard
802.11ax (WiFi 6) |
Frequency
2.4 GHz and 5 GHz |
Maximum Theoretical Speeds
9.6 Gbps |
|
WiFi Standard
802.11ax (WiFi 6e) |
Frequency
6 GHz |
Maximum Theoretical Speeds
9.6 Gbps |
|
WiFi Standard
802.11be (WiFi 7) |
Frequency
2.4, 5 and 6 GHz |
Maximum Theoretical Speeds
46 Gbps |
The 2.4 GHz frequency band offers broader coverage but slower speeds and is more susceptible to interference than 5 GHz. 5 GHz provides faster speeds and higher bandwidth but has a shorter range than 2.4 GHz. The 6 GHz band is the latest WiFi frequency band, offering faster speeds and lower latency than 5 GHz but having the shortest range.
Consider choosing a high-speed router that supports the latest WiFi standards, such as WiFi 6, to ensure faster speeds and performance, especially for a family with multiple devices performing data-intensive activities
Bandwidth capacity
The bandwidth capacity of a router determines how much data can transfer to and from the connected devices. Routers with high bandwidth capacity can handle more data traffic, maintain fast internet speeds and support multiple devices performing bandwidth-intensive activities simultaneously.
Conversely, if you have a router with a bandwidth capacity lower than your internet plan’s speed, you may experience slow internet speeds and disruptions.
For example, if you have a 1 Gig internet plan while your router only supports up to 600 Mbps, it will not be able to utilize your plan’s full speed
Router placement
The location and position of your router impacts your internet speed. Obstacles like walls, furniture, floors and other devices can obstruct WiFi signals, resulting in slow internet speeds and increased latency.
To maximize signal strength, set up your router in a central, elevated area away from obstacles and devices that emit electromagnetic interference. The stronger the WiFi signal, the more stable the internet connection and the faster the speed.

Multiple devices
Multiple devices connected to a router share the available bandwidth. The device congestion strains the router’s bandwidth and can lead to slower speeds, especially if the devices are simultaneously engaged in bandwidth-intensive activities like streaming HD content or online gaming.
Routers supporting the newer WiFi standards have a higher device capacity, allowing them to handle multiple devices simultaneously. Furthermore, modern routers offer Quality of Service (QoS) controls that enable you to prioritize traffic and allocate bandwidth to specific devices and tasks to ensure consistent network performance.

Mesh WiFi with
eero Secure
Enhanced Whole Home WiFi uses multiple routers (or eeros®) to boost range, speed, and stability, while eero Secure, included at no extra cost, offers parental controls, ad blocking, and internet backup for constant connectivity.
How modems affect internet speed
Modems are the first point of communication between your home network and your internet service provider, which is essential in determining the maximum internet speed you may get.
They come in various types, each with specific speed capabilities and compatibility requirements. The different types of modems available include:
- DSL Modems: These are used for digital subscriber line (DSL) internet connections and typically offer speeds up to 100 Mbps.
- Cable Modems: These are commonly used for cable internet services and come in different standards. These standards include the DOCSIS 3.0 modem, which handles speeds up to 1 Gbps and the DOCSIS 3.1 modem, which handles speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Fiber Modems: These are also known as Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) and are used for fiber-optic connections.
To ensure optimal performance, the modem you use must be able to handle your internet plan’s maximum speed. If your modem does not match the internet service provider’s plan, it will be a bottleneck, leading to slow internet speeds and inconsistent connections. For example, a modem that supports up to 1 Gigabit speeds will not be effective for a 5 Gigabit internet subscription.
Check with your internet service provider for the best modems that fully support your service plan’s speeds.
An outdated modem may not receive the latest firmware updates that include features that enhance network performance, leading to slower speeds and more frequent connectivity issues.
In addition, a modem’s age and condition can also impact its performance. Over time, modems can experience wear and tear, overheating or even total failure to connect.
It’s important to regularly assess the condition of your modem and consider upgrading to a newer modem to ensure you’re using the latest technology to maintain optimal internet performance.
Switch & save
Astound is the #1 cable ISP
Stream live content, work, surf, game and connect to multiple devices with speeds up to 1500* Mbps through our ultra‑reliable fiber‑powered network.*

Common issues and troubleshooting
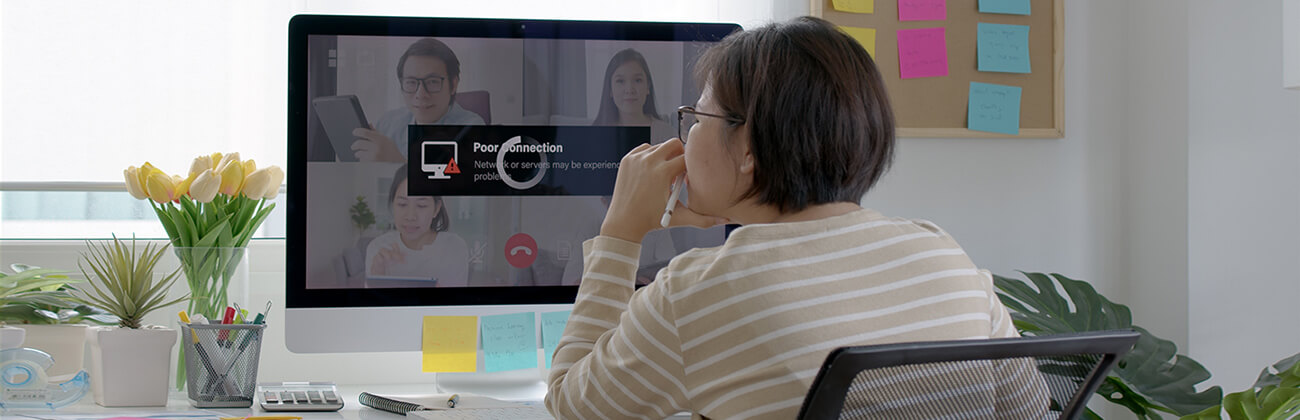
It’s essential to understand how to identify and address common problems with your router, modem or ISP if you experience speed issues. Effective troubleshooting can help you resolve speed and connectivity challenges.
Troubleshoot your devices and service
To determine if your slow internet speeds are due to your router, modem or internet service provider (ISP), follow these steps:
Step 1: Check your modem and router
-
- Test the modem directly: Disconnect your router from the modem and directly connect a device to the modem using an Ethernet cable. Test your internet speed using an internet speed test tool to see if you are getting the correct speeds from your ISP. If the speeds improve significantly, the issue is likely with your router. If the problem persists, the issue could be with the modem or your ISP.
- Router check: Check the router’s firmware and ensure it is updated. Log in to your router’s interface using a web browser or mobile application and check for firmware updates. In addition, connect to your router using an Ethernet cable and switch between the Ethernet ports while running a speed test to see if the speeds match your ISP’s advertised speeds.
- Reboot the devices: Occasionally, power cycling the router and modem can resolve speed issues. Rebooting clears the memory and resets any temporary network glitches.
Step 2: Check with your ISP
If your speeds are slow over WiFi and when using an Ethernet connection, contact your ISP’s customer service to troubleshoot the problem on their side.
- Check your ISP’s website for updates on internet outages. You may be experiencing an outage in your area. If so, you must wait for the ISP to restore internet service.
- It is vital to update your router and modem firmware regularly. Firmware updates provide new features, including performance improvements, security patches and bug fixes that can enhance your network’s performance and protect your home network from internet vulnerabilities.
Common sources of interference
Interference can significantly impact your internet speed and reliability. Common sources include:
- Wireless Devices: Microwaves, cordless phones and baby monitors can interfere with WiFi signals, especially devices that operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency.
- Physical Obstacles: Walls, floors and furniture can block or weaken WiFi signals.
- Neighboring Networks: Overlapping WiFi channels from nearby networks can cause interference.
- Distance from the router: The further you are from your router, the weaker the signal.
Learn More: What internet speed do I need?
Check for service
Get internet service that delights
Astound is ranked among the best for overall satisfaction*. When it comes to download speed and quality, Astound more than delivers.

Tips for optimizing internet speed
Optimizing your internet speed not only involves subscribing to a fast internet speed but also setting up your home network correctly to maximize the speed of your internet plan.
We’ve outlined tips you can apply to boost your internet connection’s speed.
Upgrade your devices
Upgrading to a new router or modem can significantly increase your internet speed and general network performance.
Consider upgrading to a new router if:
- Your router or modem is several years old and may not support the latest WiFi standards, such as WiFi 5 or WiFi 6, which facilitate higher speed tiers.
- You have upgraded your internet plan but are still using older equipment. Old routers may not support faster speed tiers like Gigabit speeds, so you won’t fully benefit from the increased speeds.
- Your household has added more connected devices, leading your router to struggle to handle the increased traffic and bandwidth demand. Upgrading to newer routers with higher bandwidth capacity and better processing power can handle multiple devices running simultaneously.
- You want better network security and features. Many modern routers and modems come with built-in security and performance features, such as WPA3 encryption, parental controls, firewalls and Quality of Service (QoS) options, which can improve network performance.
If you are an avid gamer, consider upgrading to a gaming router. These routers offer improved speed and performance with lower latency, advanced QoS features, broader coverage and comprehensive network customization options.
Place routers strategically
Router placement is crucial for optimizing WiFi signal strength and ensuring comprehensive coverage. Here are some best practices for optimal placement:
- Place your router centrally in your home to ensure even coverage, minimize dead zones and maintain a strong signal throughout the space.
- Elevate the router off the floor and place it on a shelf or wall. The higher placement allows the signal to travel more freely.
- Avoid obstructions like walls, floors and large furniture, which can impede the WiFi signal. Position your router in an open space, away from these barriers.
- Keep the router away from electronic devices that might cause interference, such as microwaves, cordless phones and baby monitors.

Use Ethernet cables for wired connections
While WiFi provides convenience and flexibility, wired Ethernet connections offer several advantages, particularly for tasks that require high-speed and stable internet access.
Some of the advantages of using wired connections include:
- Stable connection: Ethernet connections are less susceptible to interference and signal loss than WiFi connections. This stability is crucial for online gaming, video conferencing and streaming HD content.
- Maximum speeds: Ethernet cables provide faster internet speeds than WiFi.
- Lower latency: Wired connections typically offer lower latency than wireless ones due to less interference. Lower latency is essential for real-time applications such as gaming, live streaming and video calls.
- Security: Ethernet connections are inherently more secure than WiFi connections because they are not susceptible to wireless hacking attempts. Using a wired connection adds an extra layer of security for sensitive data transmissions.
Conclusion
Understanding how routers and modems significantly impact your internet speed is essential for optimizing your home network performance. Modems connect your home network to the ISP, translating internet signals for your router, which then distributes the internet connection and manages traffic to your devices.
Assess your network setup regularly to achieve the best internet speed possible.
Consider the age and capability of your router and upgrade to a new one that supports the latest WiFi standards. Furthermore, place the router centrally, update device firmware and use Ethernet cables for wired connections.
Investing in better network equipment can result in faster, more consistent internet speeds for all your online activities, from streaming and gaming to remote work and video calls.
Build your plan
Your perfect plan is just a click away
Get the speeds, WiFi, mobile and TV plans you need all at an affordable price. Bundle your services with Astound and see how much you can save.

Frequently asked questions
How long should a modem last?
Modems do not have a set lifespan. However, consider upgrading to a new modem every three to five years to ensure you take advantage of technological improvements that facilitate faster speeds.
Is replacing a modem easy?
Yes, replacing a modem is generally straightforward. Ensure the new modem is compatible with your ISP’s internet connection type and supports your internet speed plan. Then unplug the old modem and connect the coaxial (cable internet) or phone line (DSL) cables to the new modem, following any setup instructions provided by your ISP or the manufacturer.
Create the perfect bundle
Get the speed, WiFi, mobile and TV that’s just right for you.
*Internet speeds may vary & are not guaranteed. Certain equipment may be required to reach advertised speeds. DOCSIS 3.1 modem with 2.5GE physical LAN port is required for 1 Gigabit speeds and higher. See astound.com/yourspeed for why speeds may vary. To view Astound’s FCC Network Management Disclosure see astound.com/policies-disclaimers. Limited time offer, subject to change without notice. Advertised promotional price valid for duration of the stated promotional period from time of service activation. Regular rates apply after promotional period ends. Equipment not included and is extra. Modem required for Internet service. Enhanced Wi-Fi or Whole Home Wi-Fi (eero) not included and is add’l. Offer includes a monthly discount for enrollment in both automatic payments (autopay) & paperless billing (e-bill). Discount of $10 applies with automated bank account deduction or a discount of $5 applies with automated credit/debit card payment. Valid email address required. Must complete enrollment in autopay and e-bill within 30-days of placing the order. Without enrollment, the discount does not apply. Discount appears on bill within 3 bill cycles after enrolling. If either autopay or e-bill is canceled, services are changed, or the account is not in good standing, then the monthly discount will be discontinued. Offer valid only for new residential Astound customers or previous customers with an account in good standing who have not had Astound service within the last 60 days. Any add’l services, equipment, premium channels & other tiers of service are subject to an add’l charge & regular increases. A one-time activation fee of $14.99 (in addition to any installation fees) will be charged & is subject to change. Add’l fees apply for taxes & surcharges, and are subject to change. WA RESIDENTS: unless otherwise specified, price does not include a 2% Regulatory Administration Fee. For details about taxes, fees & surcharges visit astound.com/fees. No early termination fees apply in the event service is terminated in advance of the promotional end date. Customer is responsible for any accrued service charges in the event service is canceled. Subject to credit check. Not all services & speeds are available in all areas. A multi-product discount may be available to qualifying addresses with a subscription to mobile, TV, and 600 Mbps Internet or higher. Discounts will be reflected in your order cart at time of purchase, if available. Other restrictions may apply. All services are governed by the Astound Customer Terms & Conditions that can be found at astound.com/policies-disclaimers. © 2025 Radiate HoldCo, LLC d/b/a Astound Broadband. All rights reserved.
While we have made every attempt to ensure that the information contained in this site has been obtained from reliable sources, Astound is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for the results obtained from the use of this information. All information in this site is provided “as is”, with no guarantee of completeness, accuracy, timeliness and without warranty of any kind, express or implied, including, but not limited to warranties of performance, merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Certain links in this site connect to other websites maintained by third parties over whom Astound has no control. Astound makes no representations as to the accuracy or any other aspect of information contained in other websites.
eero Plus is available for an additional $9.99/month and requires subscription to whole home WiFi powered by eero.